Eco-Friendly HVAC Refrigerants: What Contractors Need to Know
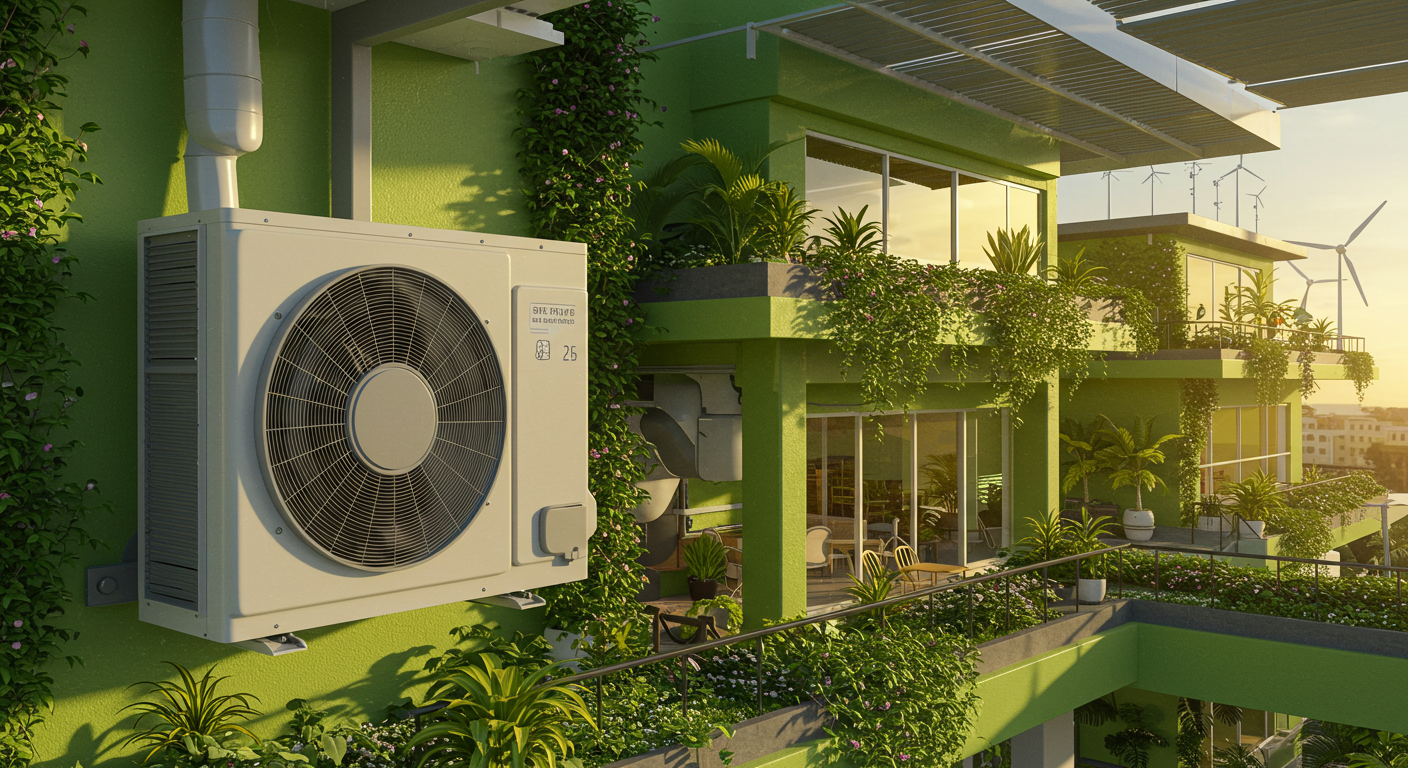
Welcome to the future of HVAC, where eco-friendly refrigerants are not just a trend but a necessity. As a contractor, you’re on the frontline of an industry in transition, and understanding sustainable HVAC refrigerants is crucial. This blog post will guide you through the essentials of low GWP refrigerants, the benefits of R32 refrigerant, and what the HVAC refrigerant transition means for you.
Understanding Eco-Friendly HVAC Refrigerants
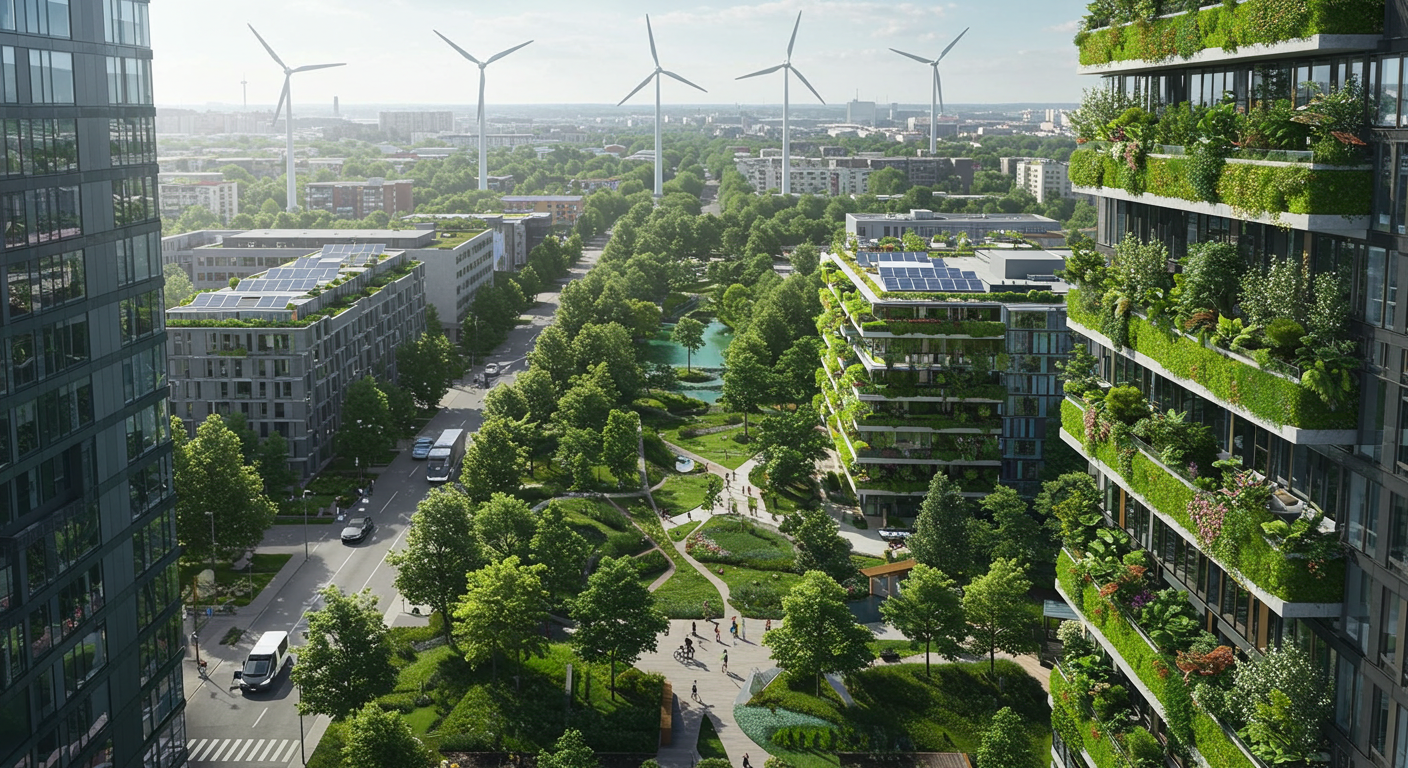
The shift towards sustainable HVAC solutions is driven by global regulations and the undeniable need to minimize the environmental impact of HVAC systems. The global low GWP refrigerant market is projected to skyrocket, growing from USD 8.7 billion in 2024 to USD 15.7 billion by 2033. This growth is fueled by regulations like the American Innovation and Manufacturing Act of 2020 and the EU’s F-Gas Regulation, which are phasing out high-GWP refrigerants.
Regional Demand and Technological Advancements
The Asia-Pacific region is leading the charge in this eco-friendly revolution, thanks to a high demand for energy-efficient cooling systems. Countries like China and Japan are not only complying with international climate rules but also actively promoting refrigerants like R-32. The development of new lubricants and CO₂ refrigeration systems is further enhancing the performance and efficiency of these sustainable solutions.
Environmental Impact and Industry Trends
Natural refrigerants such as CO₂, ammonia, and hydrocarbons are gaining popularity due to their minimal global warming potential. As the industry trends towards these alternatives, the aftermarket for low GWP refrigerants is set to expand. Consumers are increasingly opting for these solutions, drawn by their energy efficiency and reduced environmental footprint.
- Eco-friendly HVAC refrigerants are crucial for reducing environmental impact.
- Regulations are driving the adoption of low GWP refrigerants.
- Technological advancements support the transition to sustainable solutions.
- Energy-efficient HVAC refrigerants offer significant cost savings.
Compliance and Legislation
Countries worldwide are implementing legislation to phase out harmful refrigerants. For instance, Brazil is moving away from HCFCs, and companies like Carrier and Johnson Controls are expanding their products to align with these changes. It’s essential for you, as a contractor, to stay informed about these regulations to guide your clients effectively.
Conclusion
As the HVAC industry evolves, staying ahead with eco-friendly solutions is not just beneficial but necessary. By embracing low GWP refrigerants and understanding the regulations, you can provide your clients with energy-efficient and environmentally friendly options. This transition is an opportunity to lead in sustainability and innovation.
Ready to make the switch? Contact us today to learn more about eco-friendly HVAC solutions and how you can lead the way in this green revolution.
FAQ: Eco-Friendly HVAC Refrigerants
What are eco-friendly HVAC refrigerants? Eco-friendly HVAC refrigerants are substances used in cooling systems that have a lower environmental impact compared to traditional refrigerants. They are characterized by low global warming potential (GWP) and are often derived from natural sources.
Why is the HVAC refrigerant transition important? The transition is crucial for reducing the environmental impact of cooling systems and meeting global regulations aimed at minimizing greenhouse gas emissions.
What is the role of R32 refrigerant in sustainable HVAC solutions? R32 refrigerant is a popular choice due to its lower GWP compared to other options. It offers energy efficiency and is widely used in Asia-Pacific regions, setting a standard for eco-friendly HVAC solutions.
How do low GWP refrigerants impact energy efficiency? Low GWP refrigerants are designed to enhance energy efficiency, leading to cost savings on energy bills while reducing carbon footprints.
What should contractors know about HVAC refrigerant regulations? Contractors need to stay updated on national and international regulations that drive the phase-out of harmful refrigerants and ensure that their systems comply with these environmental standards.